Welcome to Pocket Science: a glimpse at recent research from Husker scientists and engineers. For those who want to quickly learn the “What,” “So what” and “Now what” of Husker research.

What?
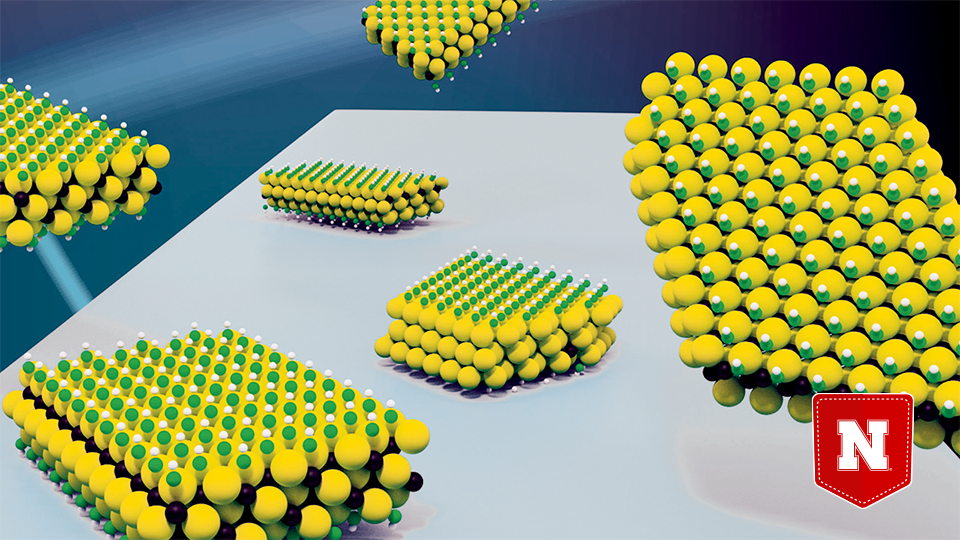
A family of 2-D nanomaterials known as MXenes has shown promise for energy storage, water purification and other applications since its discovery in 2011. Last year, Nebraska chemist Alexander Sinitskii and colleagues demonstrated a better method for synthesizing flakes of the MXene material titanium carbide, substantially boosting its electrical conductivity in the process.
The researchers have now shown that this same MXene ranks as the stiffest 2-D nanomaterial produced by solution processing, a common laboratory technique for synthesizing materials on commercially relevant scales. Titanium carbide’s resistance to mechanical forces is about 50 percent higher than its closest solution-processed counterpart.
So what?
The MXene’s stiffness means that adding it to material composites could enhance the strength and durability of protective coatings, structural components or textiles that routinely contend with the stress of mechanical forces.
Now what?








